
|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |
God decided to take the devil to court and settle their differences once and for all. When Satan heard of this, he grinned and said, -and where do you think you’re going to find a good fucking lawyer?
Recall.
For any sets X and Y, the set of all functions f : X → Y is denoted as YX = {f | f: X → Y}. Let G be a group acting on X. YX has a natural G-set structure, that is, ·: G x YX → YX, g ∈ G, f ∈ YX, g·f: X → Y is defined as the function g·f(x) = f(g·x) ∀x ∈ X.

Lemma. Let G be a group whose identity is e. Let X be a set and ·:G x X → X be a group action. Then, the set of orbits of X under the action of G, written as X/G or XG, forms a partition of X.
Proof:
Let’s define the relation x Rg y or, more succinctly, x ~ y ↭ y ∈ Orb(x) ↭ ∃g ∈ G: y = g·x. It is an equivalent relation. ∀x, y, z ∈ X:
The quotient set X/Rg, that is, the set of orbits of the group action forms a partition of X.
Notice that the equivalent class of x is [x] = {y ∈ X | x ~ y} = {y ∈ X | y ∈ Orb(x)} = {y ∈ X | ∃g ∈ G: y = g·x}
Lemma. Let x and y be two elements in X, and let g be a group element such that y = g·x. Then, the two stabilizer groups Gx = OrbG(x) and Gy = OrbG(y) are related by Gy = gGxg-1 . In other words, the stabilizers of elements in the same orbit are conjugate to each other.
Proof.
Assume that x and y are two elements in X, and let g be a group element such that y = g·x.
Let’s prove that Gy ⊆ gGxg-1. ∀h ∈ Gy ↭ h·y = y ↭[y = g·x] h·(g·x) = g·x ⇒ [Applying g-1 to both sides of this equality and taking (ii) into account yields…] (g-1hg)·x = x ⇒ g-1hg ∈ Gx ⇒ h = g(g-1hg)g-1 ∈ gGxg-1.
Next, let’s prove that gGxg-1 ⊆ Gy. y = g·x ⇒ x = g-1·y. ∀h ∈ Gx ↭ h·x = x ⇒ h·(g-1·y) = g-1·y ⇒ [Applying g to both sides of this equality yields…] (ghg-1)·y = y ↭ ghg-1 ∈ Gy ∎
Let G be a group acting on a set X. We have demonstrated that the stabilizers of elements in the same orbit are conjugate to each other, that is, Gg·x = gGxg-1, and therefore they are isomorphic to each other Gx ≋ Gg·x via an inner automorphism. In particular, if x and y are G-equivalent, then |Gx| = |Gy|
Let G be a group. For any g ∈ G, define the map cg: G → G, given by cg(x) = gxg-1. cg is an automorphism of G, and is termed as an inner automorphism.
Burnside’s Theorem. If G is a finite group acting on X, then the number k of G-orbits of X is $\frac{1}{|G|}\sum_{g∈G}|X_g|$
Proof:
Consider the equation g·x = x of two variables g ∈ G, x ∈ X. How many solutions does it have?
For each g ∈ G, the number of such pairs is $|X_g|$, so it is $\sum_{g∈G}|X_g|$. For each x ∈ X, the number of such pairs is |Gx|, so the total is $\sum_{x∈X}|G_x|$ and obviously $\sum_{g∈G}|X_g|=\sum_{x∈X}|G_x|$ 🚀
The Fundamental Counting Principle Let G be a group acting on X and x an element of X. Then, the cardinality of an orbit is equal to the index of its stabilizer, that is, |Ox| = [G:Gx]
$\sum_{y∈\mathbb{O_x}}|G_y|$ =[|Gy| = |Gx| if y ∈ $\mathbb{O_x}$ (x and y are in the same orbit)] $\sum_{y∈\mathbb{O_x}}|G_x| = |\mathbb{O_x}||G_x|$ = [The Fundamental Counting Principle] = [G:Gx]|Gx| = [By Lagrange’s Theorem] |G|. Therefore, $\sum_{y∈\mathbb{O_x}}|G_y|=|G|$
$\sum_{g∈G}|X_g|=🚀\sum_{x∈X}|G_x|$ = [Since we have just demonstrated that orbits partition X, we are going to have |G| as many times as orbits, that is, k] k|G| ⇒ k = $\frac{1}{|G|}\sum_{g∈G}|X_g|$
Examples.
Alternatively, Xid = X, X(13) = {2, 4, 5}, X((13)(25)) = {4}, X(25) = {1, 3, 4}.
The number k of G-orbits of X is $\frac{1}{|G|}\sum_{g∈G}|X_g|=\frac{1}{4}(5+3+1+3)=3$

If Y = {1, 2, 3, 4}, then D4 acts on Y in a natural way, and coloring of the vertices is a function f: Y → {B, W}. Let X = {B, W}Y = {f| f: {1, 2, 3, 4} → {B, W}}, |X| = 16, and D4 acts on X naturally. Therefore, our original question is the same as asking how many orbits does D4 have on the set of X?
|Xid| = 24 = 16. |Xr| =(1234) 2, |Xr2| =(13)(24) 4, |Xr3| =(1432) 2, |Xs| =(14)(23) 4, |Xrs| =(24) 8, |Xr2s| = 4, |Xr3s| = 8 (Figure 3).
|Xg| = 2a where 2 = |{B, W}|. a = number of cycles in the cycle decomposition of each permutation because vertices in the same cycle need to share the same color if the square was to be fixed.
| Id | r | r2 | r3 | s | rs | r2s | r3s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (1)(2)(3)(4) | (1234) | (13)(24) | (1432) | (14)(23) | (1)(24)(3) | (12)(34) | (13)(2)(4) |
| # cycles | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Xg | 16 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 |
Two designs A and B are equivalent under a group G of permutations if there is an element Φ ∈ G: Φ(A) = B, that is, they are in the same orbit of G. Therefore, the number of nonequivalent designs under G is the number of orbits of designs under G.
k = [Burnside’s Theorem] $\frac{1}{|G|}\sum_{g∈G}|X_g|$=[|Xg| = 2a where 2 = |{B, W}|. a = number of cycles in the cycle decomposition of each permutation because vertices in the same cycle need to share the same color if the square was to be fixed.] = $\frac{1}{8}(16+2+4+2+4+8+4+8)=6$ (Figure 4)

Therefore, if we could use four colors, the result would be k = [Burnside’s Theorem] $\frac{1}{|G|}\sum_{g∈G}|X_g|$=[|Xg| = 4a where a = number of cycles in the cycle decomposition of each permutation because vertices in the same cycle need to share the same color if the square was to be fixed.] $=\frac{1}{8}(4^4+4^1+4^2+4^1+4^2+4^3+4^2 +4^3) = 55$
How many ways can a tetrahedron be labeled (Figure 5)? A4 is the rotational symmetry group for the tetrahedron, |A4| = 12. It has the identity, three 2-2 cycles -each of which fixes no vertex, (12)(34), (14)(23), (13)(24)-, and eight 3-cycles -each of which fixes one vertex, e.g., we have two rotations keeping 4 fixed (132), (123), and obviously there are six rotations more which keeps vertices 1, 2, and 3 fixed.-. However, the only element that fixes any such labeling is the identity, and |Xid| = 4!, so k = [Burnside’s Theorem, a = 4] $\frac{1}{|G|}\sum_{g∈G}|X_g|=\frac{1}{12}(4!+3·0+8·0) = 2$
Given three colors, say red, green, and blue, how many ways can a cube be colored (counting rotations)? k = [Burnside’s Theorem, a = 4] $\frac{1}{|G|}\sum_{g∈G}|X_g|$
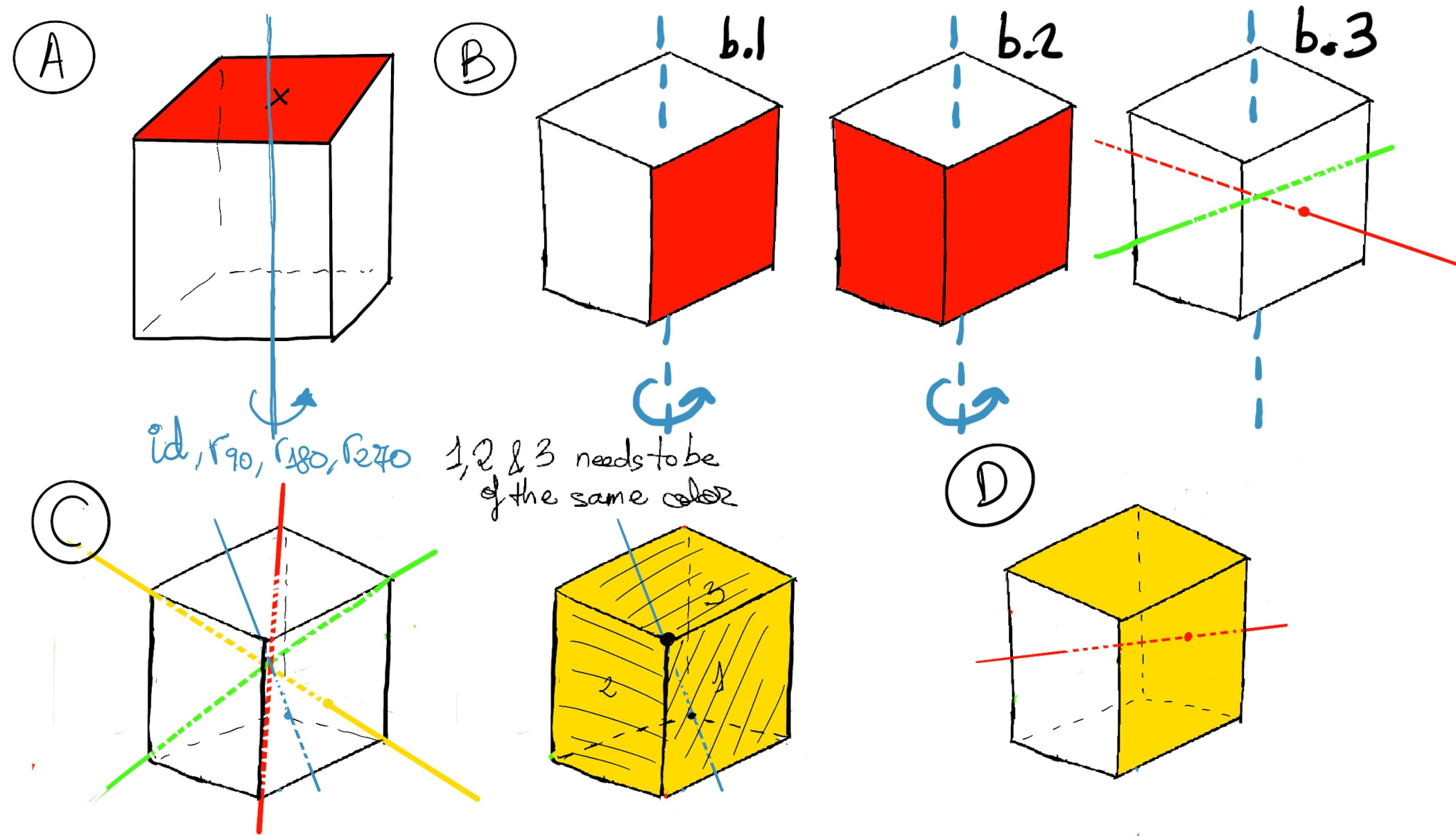
First, we need to know |G|. We are going to use the Orbit-stabilizer theorem but on a simpler action, once that simply act on the cube’s faces. Let’s pick the top face as labeled it as “x”. x can be rotated to any other face ⇒ |orbG(x)| = 6. What are the symmetries that fix this face? It could only be the group of rotation symmetries around the perpendicular axis to this face: id, r90°, r180°, and r270° ⇒ |stabG(x)| = 4 ⇒ [The orbit-stabilizer theorem] |G| = |orbG(x)|·|stabG(x)| = 6·4 = 24 (Figure A).
Let’s consider |Xid| = 36 where 3 is the number of colors available, and 6 faces of the cube.
Let’s consider a rotation about the vertical axis (Figure b). Let’s think of the rotation by 90° clockwise or counterclockwise, what does this rotation fix? Suppose that the face shown in b.1 is red, the face on the left would be rotated to the red face, so obviously the face on the left has to be red in the first place (figure b.2). Using the same argument, all four lateral faces of the cube must also share the same color, so there are 33 possibilities (32 because there are no restriction on the top and bottom faces and 3 for the shared color of the four lateral faces.) Futhermore, there are three axes (figure b.3), and for each one of them, we can rotate 90° either clockwise or anticlockwise, so we need to count this 6 times.

If we consider the same three axis, we need to consider the 180° rotation, but in this case we have more choices, because there are no restriction on the top and bottom faces, but we can also choose two different colors for two of the four lateral faces, therefore there are 34 possibilities (top + bottom + 2 laterals), and there are three of those 180° rotations.
Let’s take into account the eight rotations about the long diagonal by 120° (figure c). Faces around vertices where the rotation axis crosses need to be of the same color in order to be fixed (figure c, the faces 1, 2 and 3 need to be of the same color, as well as 4, 5, and 6), so there are only 32 possibilities, one color for each vertex.

Finally, we need to consider the six rotations passing through each pair of opposites edges (Figure D). We can chose the color for three of the faces, so there are 33 possibilities.
k = [Burnside’s Theorem, a = 4] $\frac{1}{|G|}\sum_{g∈G}|X_g| = \frac{1}{24}(3^6+6·3^3+3·3^4+8·3^2+6·3^3)=\frac{1368}{24}=57.$